Module 4: Strands of Mathematical Proficiency
EDUC 315 - Howard University
School of Education
Module Overview
This module will deepen your understanding of generating mathematical lessons with a focus on fractions and decimals.
Goals for the module
One goal for this module is for you to come up with a set of ways to describe various ways to teach students’ properties and procedural fluency. We’ll use new examples and those from previous modules to guide you.
Decimals
Decimal Place Value
For each, underline the whole number part and circle the decimal (fractional) part.
- 2.5
- 1.23
- 0.52
- 0.002
Which digit is in the tenths place? Which is in the hundredths place?
True or False: Decimal Equivalents
True or False: 25 hundredths is the same as 2 tenths and 5 hundredths?
- Draw a place value chart to prove your answer.
- Write both numbers in fraction form.
Comparing and Ordering Decimals
Compare which is greater by identifying the digits in each decimal place (tenths, hundredths, thousandths).
- 4.859
- 4.869
Next, create your own set of three decimals and order them least to greatest.
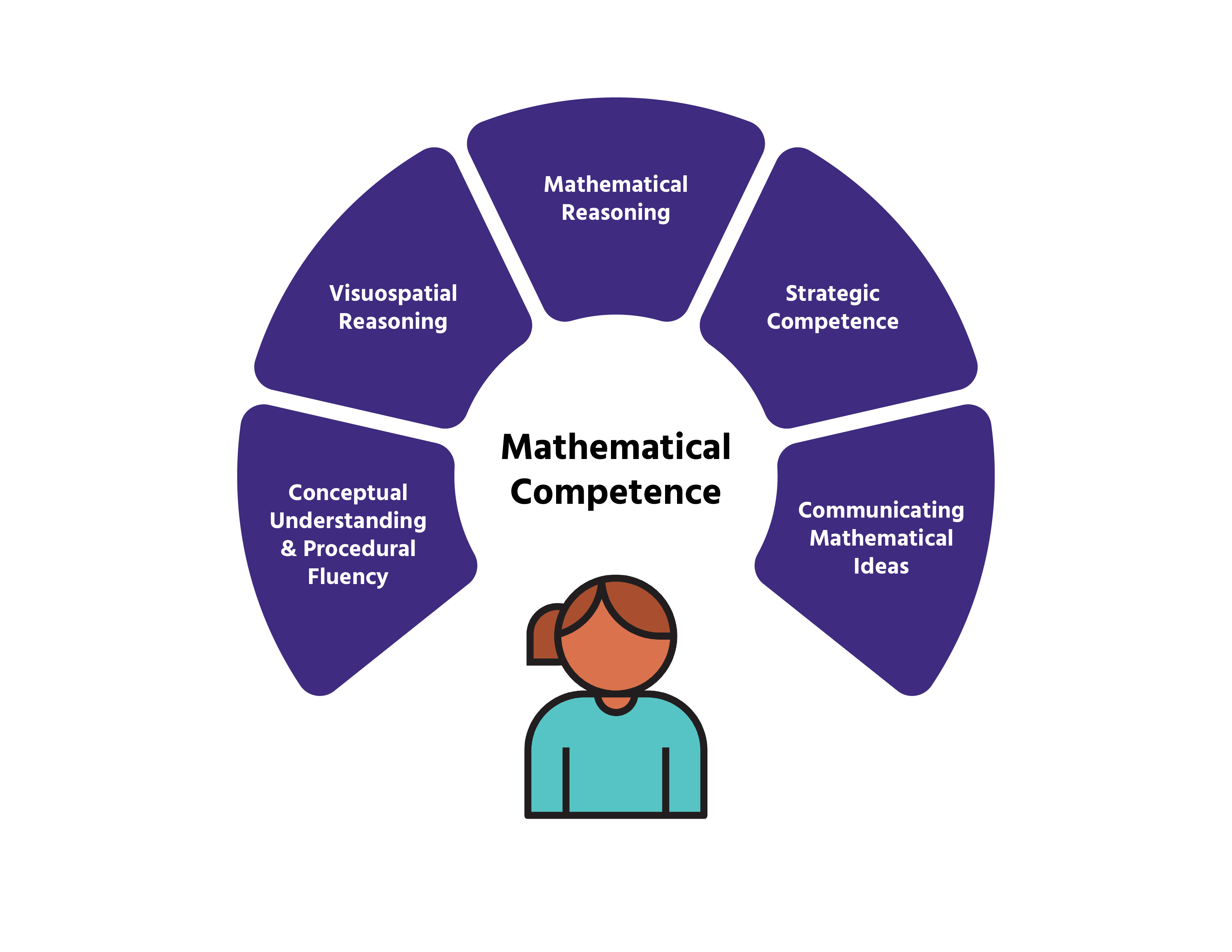
Five Strands of Mathematical Proficiency
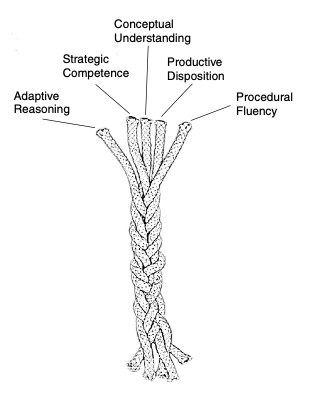
Five strands of mathematical proficiency
Kilpatrick and colleagues (National Research Council, 2001) identified five interdependent strands that together form a comprehensive definition of mathematical proficiency.
Procedural Fluency
Skill in carrying out mathematical procedures flexibly, accurately, efficiently, and appropriately.
Involves knowing procedures and using them correctly.
Includes the ability to select appropriate methods and apply algorithms based on the situation.
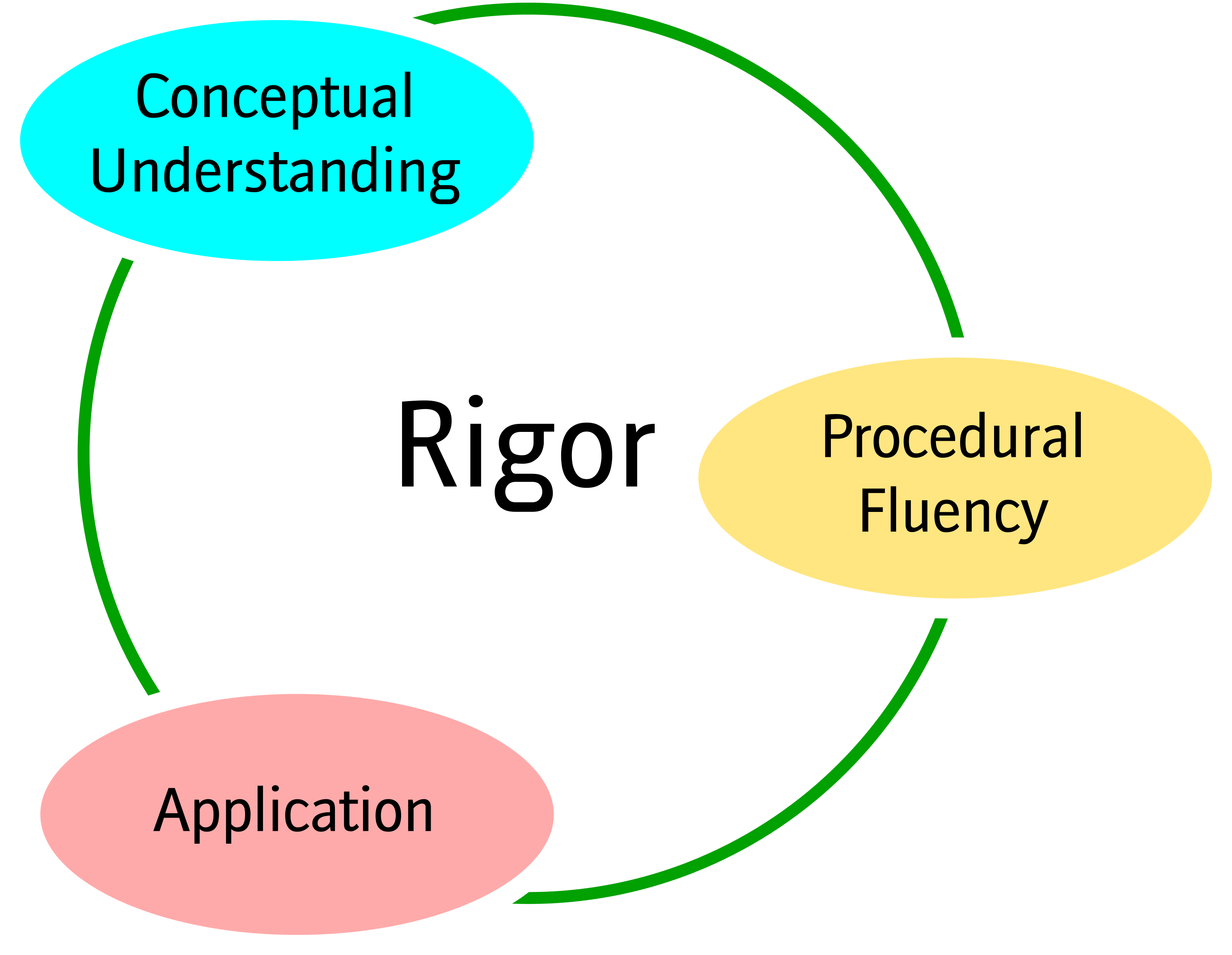
Procedural fluency
Conceptual Understanding
Comprehension of mathematical concepts, operations, and relationships.
Means having an integrated and functional grasp of ideas, not just memorizing facts.
Students should connect new knowledge with what they already know and represent mathematical situations in multiple ways.
Conceptual understanding
Adaptive Reasoning
Capacity for logical thought, reflection, explanation, and justification.
Enables students to explain and justify their strategies and solutions.
Supports the extension of knowledge from known concepts to unfamiliar situations.
Adaptive reasoning
Strategic Competence
Ability to formulate, represent, and solve mathematical problems.
Involves devising and using strategies for both routine and non-routine problems.
Encourages flexible thinking when approaching mathematical challenges.
Strategic competence
Productive Disposition
Habitual inclination to see mathematics as sensible, useful, and worthwhile, paired with a belief in perseverance and personal efficacy.
Nurtures a positive attitude and sense of efficacy towards mathematics.
Students believe that effort leads to understanding and success.
Productive disposition
| Strand | Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Procedural Fluency | Technical Performance | Memorise and rehearse |
| Conceptual Understanding | Classification, Definition | Sort, classify, define and deduce |
| Representation | Describe, interpret and translate | |
| Analysis | Explore structure, variation, connections | |
| Adaptive Reasoning | Argument, Proof | Test, justify and prove conjectures |
| Strategic Competence | Mathematical Model | Formulate models and problems |
| Solution | Employ strategies to solve a problem | |
| Critical Commentary | Interpret & evaluate solutions and strategies |
